Industry 4.0 solutions: advanced technologies for efficiency
Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, is a concept that foreshadows the future of manufacturing. This new era is transforming traditional manufacturing methods through combining digitalisation, automation and reconfigurable technologies. It aims to create smart factories that can adapt to changing market needs while optimising production processes. In our blog post, we have gathered Industry 4.0 solutions and technologies that can help increase efficiency.
The importance of Industry 4.0 lies in the fact that it revolutionises the manufacturing sector and brings efficiency, flexibility and quality to a new level. With the integration of digital technologies, factories can respond in real time to emerging challenges and quickly adapt to new products. Industry 4.0 solutions enable seamless communication between machines, sensors and systems, ensuring a continuous flow and analysis of data.
The concept is not only about technological progress but also about a change of approach in manufacturing. Instead of traditional, rigid production lines, Industry 4.0 offers flexible, modular and reconfigurable systems. This means that factories can adapt quickly to changing customer needs while optimising resource use and reducing manufacturing costs.
Industry 4.0 solutions: the pillars
Industry 4.0 is revolutionising the world of manufacturing and is based on some key technologies that together are transforming industrial production. These pillars include cyber-physical systems (CPS), the Internet of Things (IoT), big data analytics, cloud technologies, artificial intelligence and machine learning.
Cyber-physical systems
Cyber-physical systems (CPS) combine physical machines and processes in the digital world. These systems can communicate and collaborate in real-time, enabling increased flexibility and efficiency in manufacturing. CPS have a wide range of applications in industry, from production planning to quality assurance. They have the advantage of optimising processes and reducing the potential for errors but can also be challenging due to their complexity and high investment costs.
IoT
IoT, or the Internet of Things, has a key role in Industry 4.0. The IoT enables devices and machines used in manufacturing to contain sensors and be networked. These sensors collect real-time data about manufacturing processes, which can then be analysed to improve efficiency. Industrial IoT (IIoT) solutions enable companies to optimise maintenance, reduce downtime and improve product quality.
Big data
Big data and analytics are also essential for Industry 4.0. Data collection and storage allow companies to gain deeper insights into manufacturing processes. Real-time data analytics helps decision-making and predict potential problems. Predictive maintenance, for example, can use data analytics to predict machine failures, reducing unplanned downtime and improving quality assurance.
Cloud-based technologies
Cloud technologies are also gaining ground in the economy. Cloud computing enables scalability, flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Companies can store and analyse data in the cloud and access different services and platforms. This facilitates collaboration and resource sharing in manufacturing processes.
Artificial intelligence
The fifth pillar is artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, which are revolutionising manufacturing. AI can help create intelligent manufacturing processes and autonomous systems that can adapt to changing conditions. Machine learning enables the automation of quality control and failure analysis, which improves product quality and reduces scrap. The combination of AI and robotics can make manufacturing even more efficient and flexible.
Additive manufacturing (3D printing)
Additive manufacturing, more commonly known as 3D printing, is revolutionising manufacturing processes. This technology allows us to create physical objects directly from digital designs, building them layer by layer.
One of the biggest benefits of 3D printing is the freedom to design. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, additive manufacturing allows you to create parts with complex geometries and minimal material waste. This is particularly advantageous in rapid prototyping, where prototypes can be produced and tested quickly and cost-effectively. Custom component manufacturing is also a major benefit of additive manufacturing. Customised products and small batches of parts can be produced economically without the need for expensive tooling. This gives flexibility to manufacturers and allows them to better serve customer needs.
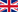
Robotics and automation
Industrial robots have been used in manufacturing for decades, but the new generation of collaborative robots (cobots) is enabling even closer collaboration between man and machine. Cobots work safely alongside humans, sensing their environment and responding intelligently to changes. They can be easily programmed and flexibly adapted to different tasks. They can be used to increase productivity and quality while reducing ergonomic risks.
Flexible production lines and intelligent material handling are also important elements of Industry 4.0. Autonomous mobile robots (AMR) can navigate in the production environment and optimise material flow. Digital twin technology can be used to virtually map and optimise production lines before they are physically implemented.
Examples of Industry 4.0 solutions
Bosch Automotive in China has combined the power of IIoT and Big Data to take digitalisation to a new level. In practice, this means that the factory's machines are equipped with sensors that continuously collect data on equipment, such as cycle times and status. This data is analysed in real-time so that it can provide useful information to staff. As a result of this innovation, there is no need to wait for a breakdown to occur and maintenance work can be carried out promptly. According to the company, there are areas where output has increased by 10% and customer satisfaction has improved.
Volkswagen is another example of Industry 4.0 solutions. The car giant has created the Automotive Cloud in partnership with Microsoft. The cloud-based storage and communication platform includes user-facing features such as digital personal assistants, predictive maintenance services and smart home connectivity.
SynerinSoft will help turn an idea into a digital reality. Let's step together on the road to Industry 4.0 - we show you the way!